
Introduction
Nursing is one of the most respected and rewarding careers, offering opportunities to make a real difference in people’s lives. However, choosing the right educational path can be challenging. Aspiring nurses often face a crucial decision: pursue an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). While both paths lead to becoming a Registered Nurse (RN), the differences in education, career opportunities, and long-term benefits can significantly influence your professional journey. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about ADN and BSN nursing.
What Is ADN Nursing?
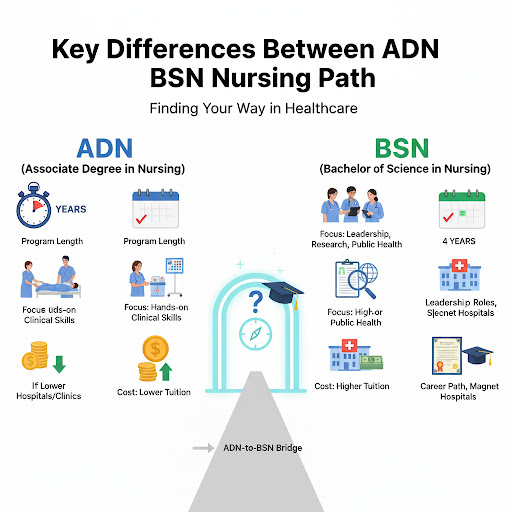
ADN Nursing refers to the Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), which is a two-year undergraduate program designed to prepare students to become Registered Nurses (RNs).
The ADN program focuses primarily on clinical skills and direct patient care, giving students hands-on experience in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings. Graduates of an ADN program are eligible to take the NCLEX-RN exam, which is required to become a licensed RN.
Key points about ADN Nursing:
- Duration: Usually 2 years.
- Focus: Practical, hands-on training in patient care.
- Education Setting: Often offered at community colleges or technical schools.
- Career Entry: Prepares students for entry-level RN positions in hospitals, long-term care facilities, and clinics.
- Cost: Typically more affordable than a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN).
ADN nursing is ideal for those who want to enter the nursing workforce quickly, gain practical experience, and later have the option to pursue a BSN through bridge programs if they want to expand career opportunities.
BSN Nursing refers to the Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), a four-year undergraduate degree that prepares students to become Registered Nurses (RNs) with a broader and more in-depth education than an ADN program.
The BSN program combines clinical training with courses in nursing research, leadership, public health, and evidence-based practice, equipping graduates for more advanced roles in healthcare.
Key points about BSN Nursing:
- Duration: Typically 4 years.
- Focus: Comprehensive education including patient care, leadership, research, and community health.
- Education Setting: Offered at universities and colleges.
- Career Entry: Prepares students for entry-level RN positions and opens doors to advanced roles such as nurse manager, educator, researcher, or policy advisor.
- Salary Potential: Often higher than ADN-prepared nurses due to advanced qualifications.
- Career Flexibility: BSN graduates are preferred by many hospitals, especially those pursuing Magnet status, and are better positioned for specialty certifications and leadership opportunities.
BSN Nursing is ideal for those who want long-term career growth, leadership opportunities, and the option to specialize in advanced areas of nursing.
What Classes Will You Take in an ADN Program?

In an ADN (Associate Degree in Nursing) program, the coursework is designed to give you the clinical knowledge and practical skills needed to work as a registered nurse. The focus is primarily on direct patient care, with some foundational sciences and general education courses. Here’s a detailed breakdown the EssayAssits way:
1. Core Nursing Courses
These courses focus on developing essential nursing skills and understanding patient care:
- Fundamentals of Nursing – Basics of patient care, hygiene, safety, and vital signs.
- Medical-Surgical Nursing – Caring for adult patients with acute and chronic illnesses.
- Pediatric Nursing – Nursing care for infants, children, and adolescents.
- Maternal-Child Nursing – Pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care.
- Mental Health Nursing – Psychiatric nursing, mental health disorders, and patient support.
- Community Health Nursing – Public health, preventive care, and working with diverse populations.
2. Anatomy and Physiology
- Understanding the structure and function of the human body is crucial for patient assessment, diagnosis, and care planning.
3. Microbiology
- Focuses on microorganisms, infection control, and disease prevention, which are essential for safe clinical practice.
4. Pharmacology
- Teaches safe medication administration, drug interactions, dosage calculations, and patient education.
5. Nutrition
- Covers dietary needs and nutritional care for patients with various health conditions.
6. Pathophysiology
- Explains the biological mechanisms of disease, helping nurses understand the “why” behind patient symptoms and treatments.
7. General Education Courses
- Most ADN programs also include general education courses such as English, psychology, sociology, and sometimes statistics to build well-rounded skills.
EssayAssits Tip:
ADN programs are intense and hands-on, with a strong focus on clinical rotations in hospitals and community health settings. While the class list is shorter than a BSN program, it equips students with all the skills needed to pass the NCLEX-RN exam and start working as an RN.
What Can You Do with an ADN Degree?

With an ADN (Associate Degree in Nursing), you are fully prepared to become a Registered Nurse (RN) and start a rewarding career in healthcare. While the ADN provides a strong foundation in clinical skills and patient care, it also offers pathways for future growth. Here’s a detailed breakdown the EssayAssits way:
1. Work as a Registered Nurse (RN)
- Primary Role: Provide direct patient care in hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, and home health settings.
- Typical Duties: Administer medications, monitor patient conditions, assist with procedures, educate patients and families, and collaborate with other healthcare professionals.
- Licensing Requirement: Pass the NCLEX-RN exam to become a licensed RN.
2. Specialize in Certain Nursing Fields
Even with an ADN, you can pursue certifications or additional training to specialize in areas such as:
- Critical Care (ICU)
- Emergency Nursing
- Pediatrics
- Geriatrics
- Medical-Surgical Nursing
Specializing often increases responsibility, expertise, and earning potential.
3. Advance Your Education Later
Many ADN-prepared nurses choose to pursue a BSN through RN-to-BSN programs:
- Allows you to continue working while completing a bachelor’s degree.
- Opens doors to management, leadership, research, and specialized roles.
- Makes you more competitive in the job market, especially in hospitals that prefer BSN-prepared nurses.
4. Career Flexibility
With an ADN, you can work in a variety of healthcare settings:
- Hospitals and surgical centers
- Long-term care facilities and nursing homes
- Outpatient clinics and physician offices
- Community health and home health care
- Telehealth and patient education services
5. Potential for Career Growth
- Starting with an ADN does not limit your career. Many nurses begin with an ADN, gain experience, and then move into higher-paying roles or pursue advanced degrees like a BSN, MSN (Master of Science in Nursing), or even nurse practitioner programs.
EssayAssits Tip:
An ADN provides a fast and practical entry into nursing, giving you hands-on experience while allowing future educational and career advancement. Whether you plan to work immediately or eventually bridge to a BSN, an ADN degree opens the door to a fulfilling, flexible, and in-demand career in healthcare.
Key Differences Between ADN and BSN Nursing:
| Feature | ADN Nursing | BSN Nursing |
| Duration | Typically 2 years | Typically 4 years |
| Education Focus | Primarily on hands-on clinical skills and direct patient care | Combines clinical skills with leadership, research, public health, and management courses |
| Cost | Generally more affordable due to shorter program length | Higher tuition due to longer program and university setting |
| Career Opportunities | Entry-level RN positions in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities | Broader opportunities including leadership, research, education, specialty nursing, and healthcare administration |
| Salary Potential | Generally lower starting salary | Often higher due to advanced qualifications and roles |
| Job Market Trends | Accepted by most hospitals; may limit advancement in some healthcare settings | Preferred or required by many hospitals, especially those seeking Magnet recognition; better prospects for promotions and specialization |
| Advancement Options | Can pursue RN-to-BSN programs later for career growth | Prepares directly for advanced roles and graduate education opportunities |
Summary:
- ADN: Faster, more affordable route to start working as an RN; ideal if you want to enter the workforce quickly.
- BSN: Longer, more comprehensive education that opens doors to leadership, research, and specialty roles in nursing; ideal for long-term career growth.
Which Path Should You Choose?

Choosing between an ADN and BSN depends on your career goals, timeline, and personal circumstances. Here’s a detailed guide the EssayAssits way:
1. Consider Your Career Goals
- ADN: Best for those who want to start working quickly and gain practical experience. If your goal is to enter the workforce fast and begin earning, an ADN is a solid choice.
- BSN: Ideal for those aiming for long-term career growth, leadership positions, or specialized nursing roles such as nurse educator, researcher, or nurse manager.
2. Think About Time and Financial Commitment
- ADN: Typically 2 years, more affordable, and allows you to start earning sooner.
- BSN: Requires 4 years of study, with higher tuition costs, but provides a broader education and potentially higher salary in the long term.
3. Evaluate Job Market Trends
- Hospitals and healthcare organizations increasingly prefer BSN-prepared nurses, especially for positions in Magnet-recognized hospitals or specialized fields.
- Starting with an ADN doesn’t prevent you from advancing; you can pursue an RN-to-BSN program later while working.
4. Long-Term Flexibility
- ADN: Offers a practical start, with the option to upgrade to a BSN later.
- BSN: Provides more direct access to advanced roles, leadership positions, and graduate education opportunities without needing additional degrees.
EssayAssits Tip:
If your immediate goal is to enter nursing quickly, an ADN is a great choice—but keep your long-term career goals in mind. If you aspire to leadership, research, or specialized clinical roles, investing in a BSN from the start may save time and open more opportunities.
Ultimately, the right path is the one that aligns with your personal goals, financial situation, and desired career trajectory. Nursing is a flexible profession, and both pathways can lead to a rewarding and impactful career.
The EssayAssits Tip
At EssayAssits, we advise aspiring nurses to think beyond graduation. While ADN programs offer a fast start, investing in a BSN can significantly impact your career trajectory, earning potential, and professional flexibility. Consider your long-term goals and how each program aligns with them.
Remember, nursing is not just a job; it’s a lifelong career where your education opens doors to leadership, research, and specialized practice. Whether you start with an ADN or a BSN, dedication, experience, and continuous learning are key to success.
Conclusion
Choosing a nursing path is one of the most important decisions for aspiring healthcare professionals. An ADN (Associate Degree in Nursing) offers a fast, affordable route into the nursing workforce, equipping students with essential clinical skills and hands-on experience. It allows you to start your career quickly, gain valuable experience, and even pursue further education through RN-to-BSN programs later.
On the other hand, a BSN (Bachelor of Science in Nursing) provides a broader, more comprehensive education, preparing nurses for leadership roles, research opportunities, and specialized positions. While it requires a longer time commitment and higher tuition, the BSN can open doors to advanced career growth and higher earning potential.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your career goals, resources, and long-term vision. Whether you start with an ADN or a BSN, both pathways lead to a fulfilling and impactful nursing career. By understanding the differences, classes, and opportunities each path provides, you can make an informed decision that sets the foundation for success in the dynamic and rewarding field of nursing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ADN Nursing

1. What is an ADN?
An ADN (Associate Degree in Nursing) is a two-year undergraduate program that prepares students to become Registered Nurses (RNs). The program emphasizes clinical skills and direct patient care.
2. How long does it take to complete an ADN program?
Typically, an ADN program takes 2 years to complete if attending full-time. Some programs may offer part-time or accelerated options.
3. Can you become a registered nurse with an ADN?
Yes. Graduates of an ADN program are eligible to take the NCLEX-RN exam, which is required to become a licensed RN.
4. What classes will I take in an ADN program?
ADN programs include courses such as:
- Fundamentals of Nursing
- Medical-Surgical Nursing
- Pediatric and Maternal-Child Nursing
- Mental Health Nursing
- Pharmacology
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Microbiology
- Nutrition
- Pathophysiology
Plus general education courses in English, psychology, and sociology.
5. What jobs can you get with an ADN degree?
An ADN qualifies you for entry-level RN positions in:
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Long-term care facilities
- Home health care
- Community health programs
You can also specialize or later pursue a BSN for more advanced roles.
6. What is the difference between ADN and BSN?
- ADN: 2-year program, focuses on clinical skills, more affordable, entry-level roles.
- BSN: 4-year degree, includes leadership, research, and public health courses, opens doors to advanced and management roles.
7. Can ADN nurses advance their careers?
Absolutely. ADN nurses can enroll in RN-to-BSN programs, pursue specialty certifications, or eventually earn advanced degrees like MSN to access leadership and higher-paying positions.
8. Is ADN nursing in demand?
Yes. There is a high demand for RNs across the U.S. and globally. Many hospitals and healthcare facilities continue to hire ADN-prepared nurses, especially for entry-level roles.
9. Which is better: ADN or BSN?
It depends on your goals:
- Choose ADN for a fast, affordable start in nursing.
- Choose BSN if you want long-term career growth, leadership, or specialized roles.
EssayAssits Tip:
Start with the path that fits your current needs and resources, but keep your long-term career goals in mind. Nursing is flexible, and you can always pursue further education or specialization later.
